Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids can feel confusing with so many conflicting health recommendations out there. If you’re an adult looking to boost your heart health, brain function, and reduce inflammation naturally, you need to know which omega-3 foods for adults pack the biggest nutritional punch.
This guide is designed for health-conscious adults who want practical, science-backed information about the best omega-3 sources without wading through complicated medical jargon. You’ll discover the top fish high in omega-3 that deliver powerful EPA and DHA, plus plant based omega-3 foods that work great for vegetarians and vegans. We’ll also cover daily intake recommendations so you know exactly how much to eat for maximum omega-3 fatty acids benefits.
Understanding Omega-3 Fatty Acids and Their Health Benefits
Essential fatty acids your body cannot produce
Omega-3 fatty acids represent a class of polyunsaturated fats that your body desperately needs but can’t manufacture on its own. Think of them as essential building blocks that must come from your diet – no exceptions. The three main types adults should know about are ALA (alpha-linolenic acid), EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid), and DHA (docosahexaenoic acid).
ALA serves as the parent omega-3 that your body can partially convert to EPA and DHA, though this conversion process is notoriously inefficient – typically less than 5% for EPA and even lower for DHA. This means relying solely on ALA sources won’t give you optimal levels of the more potent EPA and DHA forms.
EPA and DHA are the heavy hitters when it comes to omega-3 fatty acids benefits. These marine-sourced omega-3s pack the most powerful anti-inflammatory punch and deliver the most significant health improvements. Your cell membranes incorporate these fats directly, changing their flexibility and function in ways that promote better health outcomes.
Reduce inflammation and support heart health
Chronic inflammation acts like a slow-burning fire in your body, contributing to heart disease, arthritis, and numerous other health problems. Anti-inflammatory foods omega-3 rich sources work as natural fire extinguishers, cooling down this harmful inflammatory response.
EPA specifically targets inflammatory pathways by competing with omega-6 fatty acids for the same enzymes. When EPA wins this competition, your body produces less inflammatory compounds and more anti-inflammatory ones. Research shows that people consuming adequate EPA levels experience measurably lower levels of C-reactive protein and other inflammatory markers.
Your cardiovascular system reaps massive rewards from regular omega-3 consumption. These healthy fats help lower triglyceride levels by 15-30%, reduce blood pressure, improve arterial flexibility, and decrease the risk of dangerous heart rhythm abnormalities. The famous GISSI study demonstrated that heart attack survivors taking omega-3 supplements had a 20% lower risk of sudden cardiac death.
Fish high in omega-3 content provides the most bioavailable forms for heart protection. The American Heart Association recommends eating fatty fish twice weekly specifically for cardiovascular benefits.
Boost brain function and cognitive performance
Your brain tissue contains one of the highest concentrations of DHA in your entire body – about 40% of the polyunsaturated fats in your brain are DHA. This isn’t coincidental; DHA plays crucial roles in brain cell membrane structure, neurotransmitter function, and overall cognitive performance.
DHA supports the growth and maintenance of brain cells while promoting the formation of new neural connections. People with higher DHA levels consistently perform better on memory tests, processing speed assessments, and executive function evaluations. The brain’s ability to adapt and form new pathways – called neuroplasticity – depends heavily on adequate DHA availability.
Emerging research suggests that regular consumption of omega-3 foods for adults may help protect against age-related cognitive decline and reduce dementia risk. The MIND diet, which emphasizes omega-3 rich foods, has been associated with slower rates of brain aging equivalent to 7.5 years of cognitive protection.
Children and pregnant women need especially high DHA intake for proper brain development, but adults of all ages benefit from maintaining optimal levels for continued cognitive sharpness and mental clarity.
Support eye health and vision protection
DHA makes up approximately 60% of the fatty acids in your retina’s photoreceptor cells. These specialized cells convert light into electrical signals that your brain interprets as vision. Without sufficient DHA, these cells can’t function optimally, potentially leading to vision problems.
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD), the leading cause of blindness in adults over 50, shows strong connections to omega-3 intake levels. Studies indicate that people consuming the highest amounts of DHA and EPA have up to 42% lower risk of developing advanced AMD compared to those with the lowest intake.
Dry eye syndrome, an increasingly common condition in our screen-heavy world, also responds positively to omega-3 supplementation. EPA specifically helps improve tear production and reduce eye surface inflammation, providing relief for millions of sufferers.
The best omega-3 sources for eye health include fatty fish like salmon, sardines, and mackerel, which provide both EPA and DHA in optimal ratios. Regular consumption helps maintain healthy tear film, supports retinal function, and may prevent several age-related eye conditions.
Top Fish Sources Rich in EPA and DHA
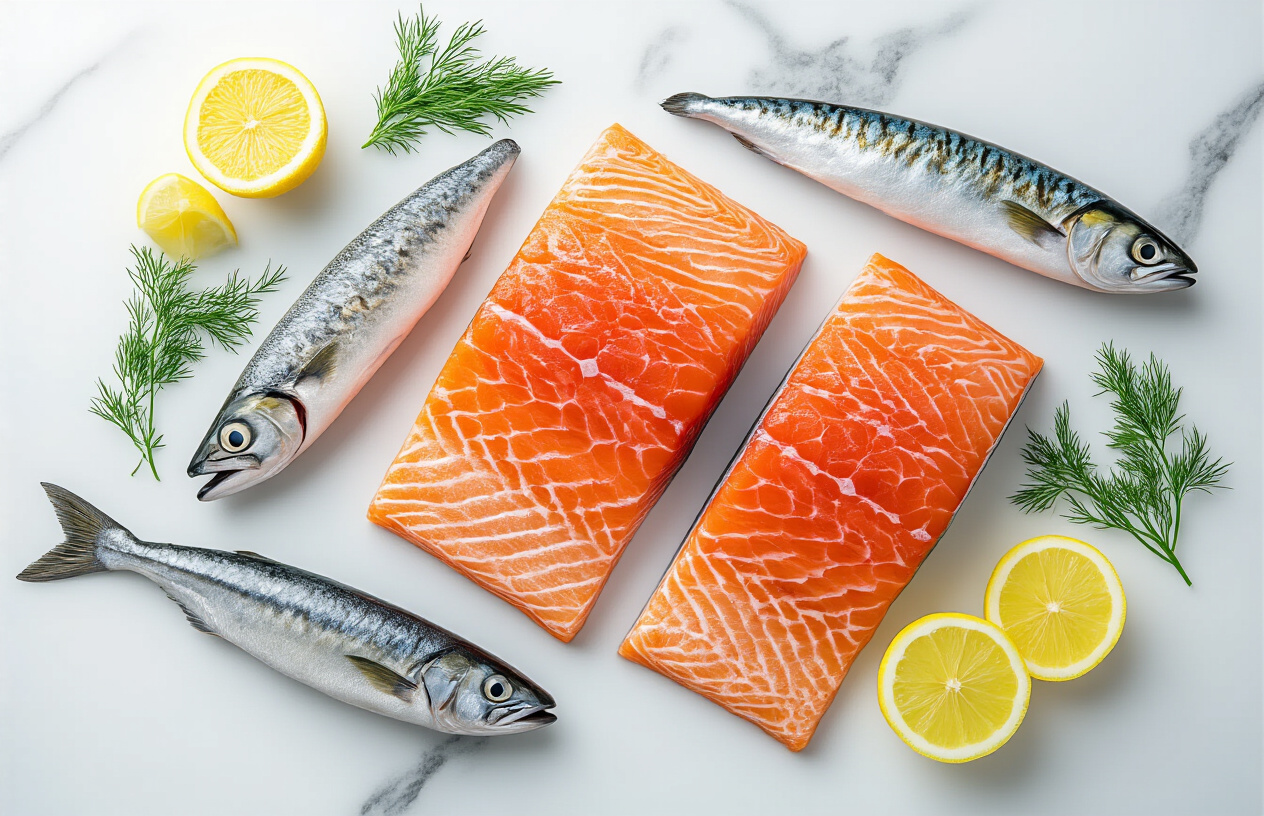

Salmon delivers maximum omega-3 concentration
Wild-caught salmon stands as the undisputed champion among EPA DHA rich foods, delivering approximately 1,200-2,400mg of omega-3 fatty acids per 3.5-ounce serving. Sockeye salmon leads the pack with the highest concentrations, followed closely by Atlantic and Coho varieties. The key difference lies in choosing wild-caught over farmed salmon, as wild varieties contain significantly higher omega-3 levels and better omega-3 to omega-6 ratios.
Atlantic salmon provides about 2,260mg of combined EPA and DHA, while pink salmon offers around 1,210mg per serving. The rich, buttery texture makes salmon incredibly versatile – perfect for grilling, baking, or enjoying as sashimi. Most nutritionists recommend consuming salmon 2-3 times per week to maximize omega-3 intake.
Sardines provide affordable nutrient density
Don’t overlook these tiny powerhouses when seeking omega-3 foods for adults. Sardines pack an impressive 1,480mg of EPA and DHA per 3.5-ounce serving, making them one of the most cost-effective sources available. Fresh sardines from Portugal or Spain offer superior taste, while canned varieties provide convenience without sacrificing nutritional value.
Beyond omega-3s, sardines deliver exceptional amounts of vitamin D, calcium, and vitamin B12. Their small size means lower mercury accumulation compared to larger fish, making them safer for frequent consumption. Try grilled fresh sardines with lemon and herbs, or add canned sardines to salads and pasta dishes for an instant omega-3 boost.
Mackerel offers high levels with great taste
Atlantic mackerel contains approximately 2,670mg of omega-3 fatty acids per serving, ranking among the best omega-3 sources in the seafood world. King mackerel and Spanish mackerel also provide substantial amounts, though Atlantic mackerel typically offers the highest concentration.
The rich, distinctive flavor pairs beautifully with citrus marinades and bold spices. Smoking or grilling brings out mackerel’s natural oils, creating a satisfying meal that delivers significant anti-inflammatory benefits. Choose smaller mackerel when possible, as they contain less mercury while maintaining peak omega-3 levels.
Anchovies pack powerful nutrition in small portions
These small fish high in omega-3 deliver about 1,040mg per 3.5-ounce serving, but their intense flavor means a little goes a long way. White anchovies offer milder taste than their salt-cured counterparts, making them more appealing to sensitive palates.
Fresh anchovies work wonderfully in Mediterranean dishes, while canned varieties add depth to Caesar dressings, pizza toppings, and pasta sauces. Their concentrated nutrition profile includes high-quality protein, selenium, and niacin alongside substantial omega-3 content.
Tuna provides convenient omega-3 options
Albacore tuna offers approximately 1,400mg of omega-3s per serving, while bluefin tuna can contain up to 1,600mg. Fresh tuna steaks provide maximum omega-3 benefits, though canned albacore tuna packed in water still delivers meaningful amounts.
Due to mercury concerns, limit tuna consumption to 2-3 servings per week. Choose pole-and-line caught tuna when possible for both environmental sustainability and potentially lower mercury levels. Seared ahi tuna or tuna sashimi maximizes omega-3 retention compared to heavily cooked preparations.
Plant-Based Omega-3 Powerhouses
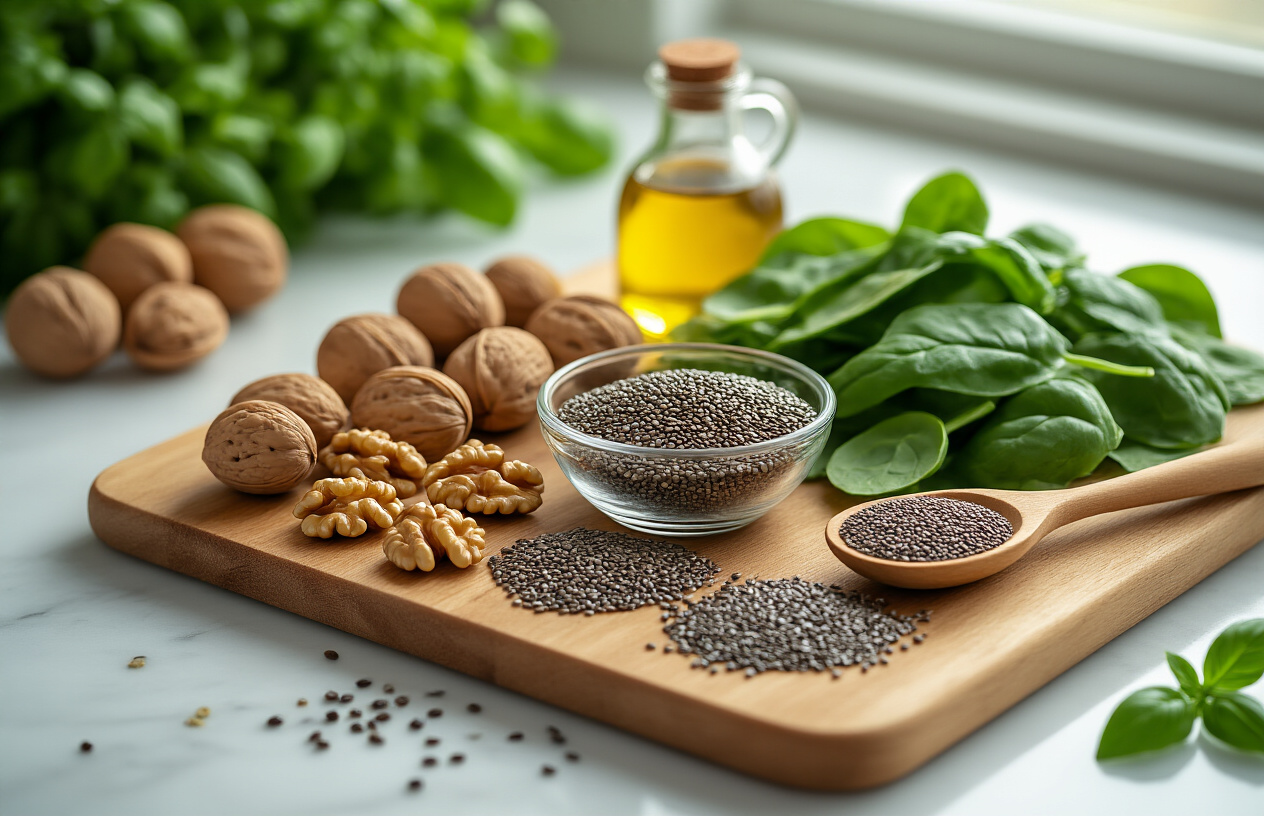

Flaxseeds offer versatile ALA-rich nutrition
Flaxseeds pack an impressive punch when it comes to plant based omega-3 foods, containing more alpha-linolenic acid (ALA) per serving than almost any other food source. Just two tablespoons of ground flaxseeds deliver about 3.2 grams of omega-3 fatty acids, making them one of the most concentrated plant-based sources available.
Ground flaxseeds work better than whole seeds because your body can’t break down the tough outer shell of whole flaxseeds. You can easily add ground flaxseeds to smoothies, yogurt, oatmeal, or baked goods. They have a mild, nutty flavor that won’t overpower your favorite dishes. Store ground flaxseeds in the refrigerator to prevent the oils from going rancid.
Chia seeds provide complete protein plus omega-3s
These tiny black or white seeds might look unassuming, but chia seeds contain about 2.5 grams of ALA omega-3s in just one ounce. What makes chia seeds special among omega-3 foods for adults is their complete amino acid profile, meaning they provide all nine essential amino acids your body needs.
Chia seeds become gel-like when mixed with liquid, making them perfect for puddings, smoothies, and as an egg substitute in baking. Unlike flaxseeds, you don’t need to grind chia seeds to access their nutrients. They’re also loaded with fiber, calcium, and magnesium, giving you multiple nutritional benefits in one small package.
Walnuts deliver brain-boosting healthy fats
Walnuts stand out among nuts as the only tree nut that’s an excellent source of ALA omega-3s. A quarter-cup serving provides roughly 2.7 grams of these essential fatty acids. Research shows that regular walnut consumption may support brain health and cognitive function, earning them the nickname “brain food.”
The convenience factor of walnuts makes them ideal for busy adults. You can eat them straight from the bag as a snack, chop them into salads, or blend them into homemade nut butter. Their rich, slightly bitter flavor pairs well with both sweet and savory dishes.
Hemp seeds combine omega-3s with minerals
Hemp seeds, also called hemp hearts, offer a unique nutritional profile that includes omega-3 fatty acids alongside important minerals like magnesium, iron, and zinc. Three tablespoons contain about 1 gram of ALA omega-3s plus a substantial amount of protein – roughly 10 grams.
These small, nutty-tasting seeds have a soft texture that makes them easy to digest. You can sprinkle hemp seeds on salads, blend them into smoothies, or eat them by the spoonful. They don’t require any special preparation and have a long shelf life when stored properly.
Specialty Foods and Fortified Options

Omega-3 Enriched Eggs from Pasture-Raised Hens
When you’re looking for easy ways to boost your omega-3 intake, specialty eggs deserve a spot on your grocery list. These aren’t your regular supermarket eggs – they come from hens that eat flax seeds, fish meal, or algae-rich diets, which naturally increases the omega-3 content in their eggs.
A single omega-3 enriched egg typically contains 100-200mg of omega-3 fatty acids, compared to just 40mg in conventional eggs. The difference is significant enough to make these specialty eggs worth the extra cost. Pasture-raised hens that roam freely and eat omega-3 rich foods produce eggs with even higher nutritional value.
You’ll find these eggs clearly labeled in most grocery stores, often with terms like “omega-3 enriched,” “high in omega-3,” or “from flax-fed hens.” The shells might be brown or white – color doesn’t affect the omega-3 content. These eggs taste virtually identical to regular eggs, so you can scramble, poach, or bake with them just like any other egg.
Algae-Based Supplements for Vegetarians and Vegans
Plant-based omega-3 supplements offer a game-changing solution for those avoiding fish products. These supplements extract omega-3s directly from marine algae – the same source that fish get their EPA and DHA from in the wild.
Algae oil supplements provide both EPA and DHA, the two most beneficial omega-3 fatty acids that are typically only found in fish. This makes them particularly valuable for vegans and vegetarians who might otherwise struggle to get adequate amounts of these essential fatty acids from food alone.
Quality algae-based supplements can provide 250-500mg of combined EPA and DHA per capsule. The oil is typically odorless and doesn’t cause the fishy aftertaste that some people experience with traditional fish oil supplements. Many brands now offer algae oil in softgel form, making them as convenient as any other supplement.
These supplements undergo rigorous testing for purity and potency, often exceeding the quality standards of fish-based alternatives. They’re also more environmentally sustainable, requiring no fishing or marine habitat disruption.
Fortified Dairy Products Boost Daily Intake
The dairy aisle now offers several omega-3 fortified options that make increasing your intake surprisingly simple. Milk, yogurt, and even some cheeses now come enriched with these healthy fats, turning everyday foods into omega-3 powerhouses.
Fortified milk typically contains 32-50mg of omega-3s per 8-ounce serving, while omega-3 enriched yogurt can provide 50-100mg per cup. These numbers might seem modest compared to fish sources, but they add up quickly when you’re already consuming these foods regularly.
Greek yogurt brands often lead the way in fortification, combining high protein content with added omega-3s. Some manufacturers use fish oil for fortification, while others opt for algae oil to appeal to vegetarian consumers. Always check labels to understand the source if you have dietary restrictions.
Fortified dairy products maintain their familiar taste and texture, making them perfect for people who want omega-3 benefits without changing their eating habits. You can continue enjoying your morning cereal with fortified milk or afternoon yogurt snack while secretly boosting your omega-3 intake.
| Product Type | Typical Omega-3 Content | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Enriched Eggs | 100-200mg per egg | Daily breakfast routine |
| Algae Supplements | 250-500mg per capsule | Vegetarians/vegans |
| Fortified Milk | 32-50mg per 8oz | Regular dairy consumers |
| Omega-3 Yogurt | 50-100mg per cup | Snacking and meals |
Daily Serving Recommendations and Practical Tips

Optimal weekly fish consumption guidelines
Most health organizations recommend eating fish twice per week to meet your omega-3 daily intake recommendations. The American Heart Association suggests at least two servings of fish high in omega-3 weekly, with each serving weighing around 3.5 ounces. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, sardines, and tuna pack the most EPA and DHA punch per serving.
For maximum health benefits, aim for about 8-12 ounces of seafood weekly. Pregnant women should stick to 8-10 ounces and choose low-mercury options like salmon, anchovies, and sardines. If you’re vegetarian or vegan, you’ll need to focus more heavily on plant based omega-3 foods and consider algae-based supplements to get adequate EPA and DHA.
Portion sizes for maximum health benefits
A standard serving of fish equals about 3.5 ounces cooked, roughly the size of your palm. This portion typically provides 1,000-2,000 mg of combined EPA and DHA. Smaller fatty fish like sardines require about 4-5 whole fish per serving, while a piece of salmon should measure about 4×3 inches and 3/4 inch thick.
For omega-3 foods for adults, here’s what optimal portions look like:
- Walnuts: 1 ounce (14 halves) provides 2.5g ALA
- Chia seeds: 1 tablespoon delivers 1.9g ALA
- Flaxseeds: 1 tablespoon ground provides 1.6g ALA
- Hemp seeds: 3 tablespoons offer 2.6g ALA
Remember that plant sources provide ALA, which your body converts to EPA and DHA at only 5-15% efficiency.
Simple meal planning strategies
Planning your omega-3 intake becomes easier when you batch prep and rotate different sources throughout the week. Start with “Meatless Monday” featuring a walnut and spinach salad, then add “Fish Friday” with baked salmon.
Keep canned sardines, salmon, and tuna in your pantry for quick meals. These shelf-stable options work perfectly in pasta dishes, on toast, or mixed into salads. Frozen fish fillets cook quickly and maintain their nutritional value when flash-frozen properly.
Create a weekly rotation system:
- Monday: Chia seed pudding for breakfast
- Wednesday: Sardine avocado toast for lunch
- Friday: Grilled salmon for dinner
- Sunday: Walnut-crusted chicken for meal prep
Sprinkle ground flaxseed on yogurt, oatmeal, or smoothies daily. This simple habit adds omega-3s without changing your existing routine.
Storage and preparation methods to preserve nutrients
Proper storage protects delicate omega-3 fatty acids from oxidation and rancidity. Store fresh fish in the coldest part of your refrigerator and use within 1-2 days. Wrap it tightly in plastic wrap or place in airtight containers to prevent air exposure.
Frozen fish maintains quality for 3-6 months when stored at 0°F or below. Thaw frozen fish gradually in the refrigerator, never at room temperature, to preserve texture and nutrients.
For cooking methods that preserve EPA DHA rich foods, choose:
- Baking: Gentle heat maintains omega-3 integrity
- Steaming: No added fats needed, nutrients stay intact
- Poaching: Low-temperature cooking preserves delicate oils
- Grilling: Quick cooking time minimizes nutrient loss
Avoid deep frying, which can damage omega-3 structures and add unhealthy fats. When pan-searing, use medium heat and healthy oils like olive oil.
Store nuts and seeds in airtight containers in cool, dark places. Refrigerate opened packages of walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds to prevent rancidity. Ground flaxseed should always live in the freezer since grinding exposes more surface area to air and light.
Buy smaller quantities of perishable omega-3 sources more frequently rather than bulk purchasing, ensuring you consume them while they’re fresh and nutritionally potent.

Getting enough omega-3 fatty acids doesn’t have to be complicated. Fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines pack the most punch with EPA and DHA, while plant-based options like chia seeds, flaxseeds, and walnuts offer ALA that your body can convert. Don’t overlook specialty foods like algae supplements or fortified eggs and yogurt – they’re great alternatives if you’re not a fan of fish or follow a plant-based diet.
Start small and build these foods into your routine gradually. Aim for two servings of fatty fish per week, sprinkle some chia seeds on your morning yogurt, or swap out regular eggs for omega-3 enriched ones. Your heart, brain, and joints will thank you for making these simple swaps. The key is consistency – pick the omega-3 sources that fit your taste and lifestyle, then make them a regular part of your meals.









